Maternity Child Health

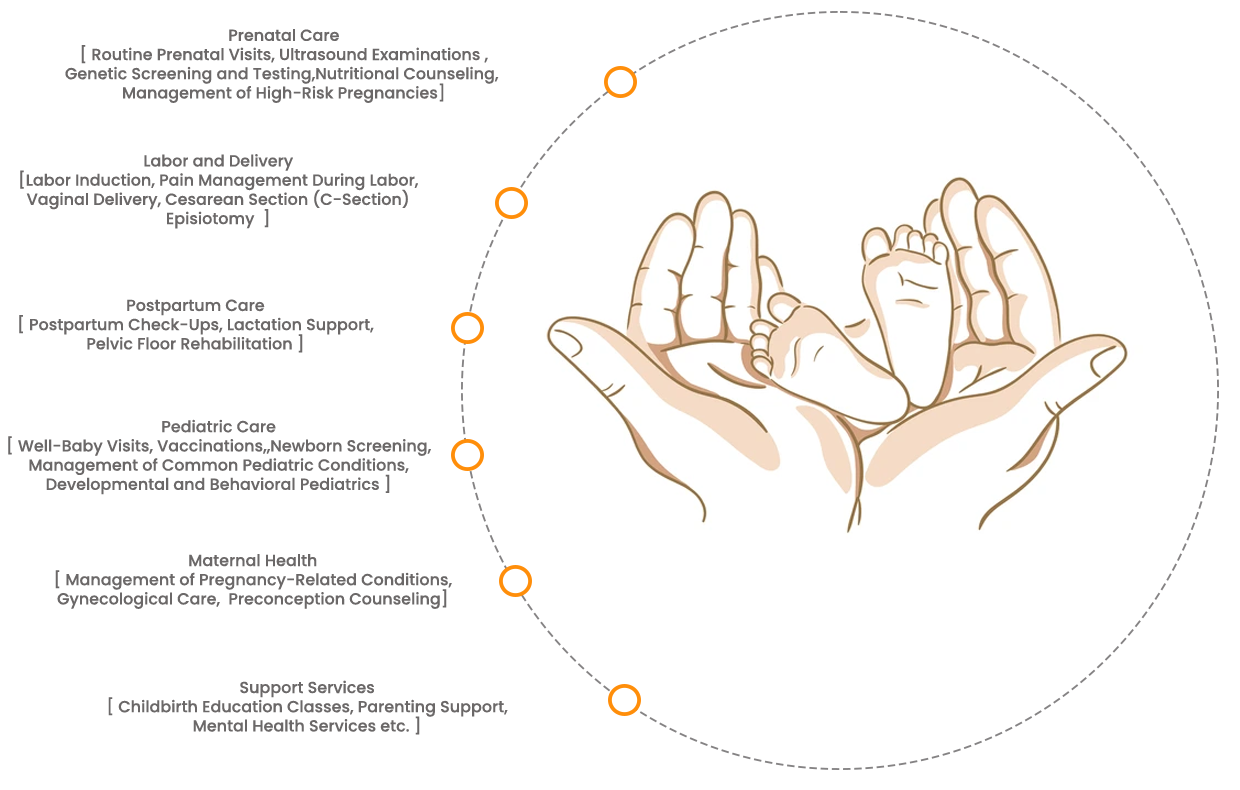
Regular Check-ups: Routine visits to monitor the health of the mother and the developing fetus, including ultrasounds and blood tests.
Nutritional Support: Guidance on a balanced diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals to support pregnancy.
Supplements: Prescribed vitamins and minerals, such as folic acid and iron, to prevent deficiencies and complications.

Gestational Diabetes Management: Monitoring blood sugar levels, dietary modifications, exercise, and possibly insulin therapy.
Preeclampsia Management: Close monitoring of blood pressure, medications to lower blood pressure, and in severe cases, early delivery.
Preterm Labor Management: Medications to delay labor, steroids to accelerate fetal lung development, and specialized care for premature infants.

Postpartum Hemorrhage Treatment: Medications to contract the uterus, blood transfusions if necessary, and surgical interventions.
Postpartum Depression Treatment: Counseling, support groups, and medications such as antidepressants.
Infection Treatment: Antibiotics for bacterial infections and proper hygiene practices to prevent infections.

Surgical Correction: Procedures to correct structural abnormalities, such as heart defects or cleft palate.
Therapies: Physical, occupational, and speech therapies to address developmental challenges.
Specialized Care: Ongoing medical care and support for managing conditions like Down syndrome.

Balanced Diet Plans: Personalized dietary recommendations to ensure adequate nutrient intake.
Supplements: Iron, vitamin D, and other essential nutrients to address deficiencies.
Breastfeeding Support: Guidance and support for breastfeeding to ensure proper infant nutrition.

Vaccinations: Immunizations to protect against diseases like measles, polio, and whooping cough.
Antibiotics: Medications to treat bacterial infections.
Hydration and Nutrition: Ensuring adequate fluids and nutrition during illness to prevent dehydration and support recovery.

Asthma Management,Allergy Management, Diabetes Management

Gestational Diabetes: A type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy and can affect the health of both the mother and baby.
Preeclampsia: A condition characterized by high blood pressure and signs of damage to another organ system, often the kidneys.
Preterm Labor: Labor that begins before the 37th week of pregnancy, which can lead to premature birth and associated health issues.

Postpartum Hemorrhage: Excessive bleeding following childbirth, which can be life-threatening if not managed promptly.
Postpartum Depression: A severe form of depression that occurs after childbirth, affecting a mother’s ability to care for herself and her baby.
Infections: Postnatal infections can occur in the uterus, bladder, or breasts (mastitis), impacting maternal health.

Congenital Heart Defects: Abnormalities in the structure of the heart present from birth, affecting normal heart function.
Neural Tube Defects: Birth defects of the brain, spine, or spinal cord, such as spina bifida and anencephaly.
Down Syndrome: A genetic disorder caused by the presence of an extra chromosome 21, leading to developmental and physical changes.

Malnutrition: Inadequate nutrition leading to stunted growth, weakened immunity, and developmental delays.
Iron Deficiency Anemia: A common condition where a lack of iron leads to reduced red blood cell production, causing fatigue and weakness.
Vitamin D Deficiency: Insufficient vitamin D can lead to bone problems like rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults.

Respiratory Infections: Common infections like pneumonia and bronchitis can be severe in young children.
Diarrheal Diseases: Often caused by infections, these can lead to dehydration and malnutrition in children.
Vaccination-Preventable Diseases: Diseases like measles, polio, and whooping cough can be prevented through immunization.

Asthma: A chronic lung condition that causes difficulty breathing due to inflamed airways.
Allergies: Hypersensitive reactions to substances like pollen, food, or dust mites, causing symptoms ranging from mild to severe.
Diabetes: A chronic condition where the body cannot properly regulate blood sugar levels.

Autism Spectrum Disorders: A group of developmental disorders affecting communication, behavior, and social interaction.
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): A disorder marked by an ongoing pattern of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity.
Speech and Language Delays: Delays in the development of speech and language skills, affecting communication.

Failure to Thrive: A condition where a child does not gain weight or grow as expected.
Stunting: Impaired growth and development due to chronic malnutrition.
Delayed Milestones: When a child does not reach developmental milestones at the expected times.

Hypertension: High blood pressure during pregnancy, which can lead to complications like preeclampsia.
Anemia: A condition where there are not enough healthy red blood cells to carry adequate oxygen to the body’s tissues.
Mental Health Disorders: Conditions such as anxiety and depression that can affect maternal well-being.

Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS): The sudden, unexplained death of a healthy baby, usually during sleep.
Pediatric Cancers: Cancers that occur in children, such as leukemia, brain tumors, and lymphoma.
Obesity: Excessive body fat that can negatively impact a child’s health and well-being.

 facebbok
facebbok
 whatsapp
whatsapp
 instagram
instagram
 youtube
youtube